
The Amazon jungle approaches inflection points and would become a savannah
According to an investigation published in the Geophysical Research Letters magazine, this ecosystem could be approaching a turning point that, in less than a century, could transform it into a dry savanna. The team in total identified three inflection points.
A new study reveals a disturbing panorama for the Amazon, the largest tropical jungle in the world. According to an investigation published in the Geophysical Research Letters magazine, this ecosystem could be approaching a turning point that, in less than a century, could transform it into a dry savanna. In addition, it plays a key role in the global cycles of water and carbon, regulating the climate. In recent years, tropical jungles, such as the Amazon, have shown vulnerability to forest droughts and fires, driven by climate change and deforestation. Only in 2024, the Brazilian Amazon lost 28,000 km² of forest coverage, according to the most recent report of the World Resources Institute. To evaluate how this ecosystem would respond to the combination of climate change and deforestation, a team of researchers, led by Andrew Friend, professor of terrestrial systems at the University of Cambridge, used a computer model. The simulation represented an average point within the Amazon basin, covering the area where the Amazon River and its tributaries flow. Based on the results, the team of researchers identified three turning points: a 65 % decrease in forest coverage, a 10 % reduction in moisture from the Atlantic and a 6 % drop in rainfall. Specialized in science, Friend explained that beyond these thresholds, small changes in climate or forest coverage of the region could take the forest to the limit, transforming this ecosystem into a meadow. The main reason, the researcher added, is because the phenomenon would be driven by a feedback cycle between the earth, vegetation and atmospheric humidity. Trees absorb soil water and release steam through evaporation and perspiration. That steam is condensed in the atmosphere and rain shape, which returns to the ground to feed the trees, and thus the cycle continues, the researcher noted. But if there are fewer trees, there is less evapotranspiration, less rain and, consequently, the forest dries and becomes savanna. This change may be due to deforestation, but climate change can also cause it, which alters the total amount of water that enters the basin from the Atlantic Ocean, said Live Science. While adjusting the tool, the authors of the study warn that it is urgent to take measures to prevent the Amazon from crossing this threshold.
IT MAY INTEREST YOU
 The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
Pioneering study shows trees surprising internal microbial diversity and potential influence on global climate, driving novel strategies for agricultural and forestry management
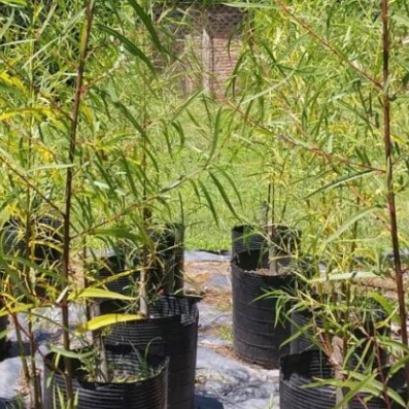 INTA Delta begins propagation of seven Creole willow clones for ecological restoration in Paraná
INTA Delta begins propagation of seven Creole willow clones for ecological restoration in Paraná
As a result of the rescue, domestication and registration work carried out by Teresa Cerrillo, a leading researcher in Salix Genetic Improvement, within the framework of the National Genetic and Forest Resources Programs of INTA, the multiplication and propagation of seven clones of Creole willow (Salix humboldtiana) began recently registered in the National Seed Institute (INASE) by INTA Delta del Paraná.
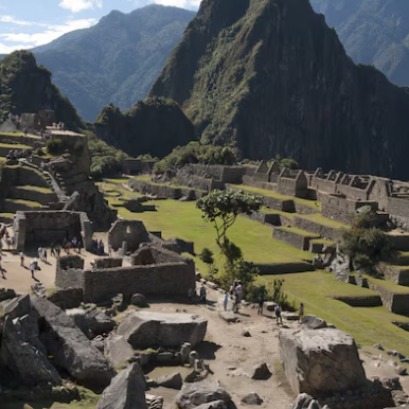 Reforestation advances in the Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu with new restored hectares
Reforestation advances in the Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu with new restored hectares
The plan includes the planting of a thousand new trees in the sanctuary, in response to the damage caused by forest fires and environmental threats, with the support of local authorities and representatives of the tourism sector.





















