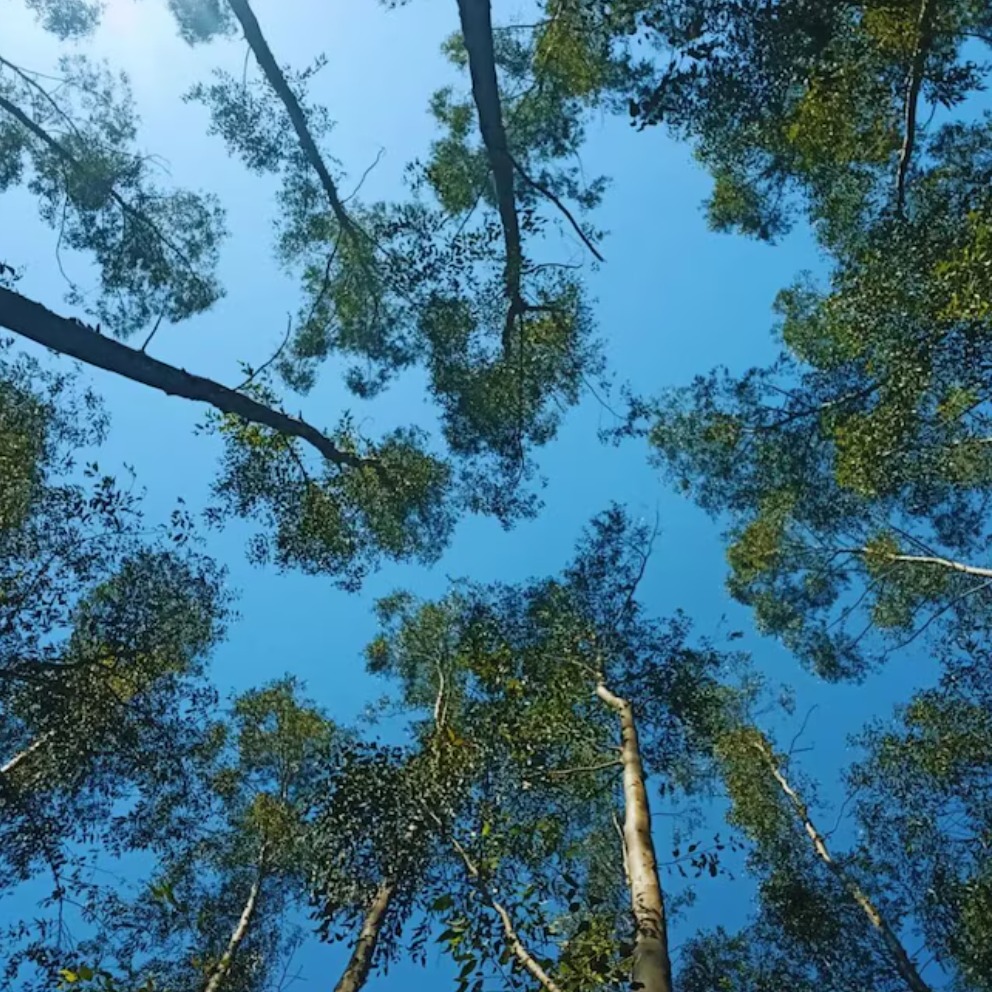

Eucalyptus: a forest bet with great future in the Chaco
It is emerging as a profitable and sustainable afforestation option. With its rapid growth and great adaptability, it promises to transform the forest production of the province and open new doors to local economic development is emerging as a profitable and sustainable afforestation option. With its rapid growth and great adaptability, it promises to transform the forest production of the province and open new doors to local economic development in the heart of the Chaco, the eucalyptus begins to change the landscape.
It stands out between the vast and aggregate fields, with its silver bark that reflects the noon sun. The leaves, of a green-blue, move gently with the breeze, releasing its characteristic aroma. As the plantations grow, these trees reach impressive heights, adding a new element to the Chaco environment. With its rapid development, it is positioned as a promising option for the productive future of the region. Fast growth species, such as eucalyptus, not only produce large amounts of wood in a short time, but also have the ability to adapt to various climates and soils. In different parts of the world, eucalyptus proves to be a perfect ally for afforestation, and the Chaco is no exception. However, the success of this practice depends on selecting adequate species and creating optimal conditions for its development. Fortunately, the province begins to adapt to the best practices of other regions and adjust them to its own context. that combine characteristics such as pest resistance, rapid growth, wood density and frost tolerance. These clones are a kind of: superspecie designed to be more productive and resistant, which allows them to better adapt to the Chaco climate and the challenges of the industry. Although advances are hopeful, the path to successful afforestation is still under construction. Forest engineer Marcos Atanasio, specialist of INTA Sáenz Peña, points out that in Chaco experiences with rapid growth species are limited. However, the results of the first essays are positive, which generates optimism in the province. Compared to other regions with more experience in afforestation, in Chaco we are learning, but the results are encouraging, says Atanasio.A field of research with much by explorardes of 2015, INTA carries out essays to study which eucalyptus species adapt better to local conditions. The first data show that eucalyptus could be a successful alternative for the downtown area of ??the province, provided that studies are continued to other areas. More than 49 clonal materials of eucalyptus are being evaluated in terms of survival, growth, and resistance to pests and frosts. While the initial results are promising, it is crucial Construction. In addition to producing wood for posts, struts and rods, the species has applications in the sawing industry, the production of paper pulp and energy biomass. These diversified uses allow eucalyptus to think as a comprehensive option, capable of contributing to the energy sustainability and productive diversification of the province. A future full of possibilities of forestry with eucalyptus could transform the productive panorama of the Chaco. With its rapid growth cycle and versatility, this species has the potential to become one of the most important in the region. However, to take advantage of its full potential, it is necessary to continue investigating and expanding studies in other areas of the province. If everything follows its course, eucalyptus could become much more than a tree in the Chaco landscape. It would be a source of employment, development and sustainability. An opportunity for a Chaco that reinvents itself, looking for new ways of growing and betting on a greener and prosperous future.
IT MAY INTEREST YOU
 The DNA of forests: they discover what makes a tree resist drought
The DNA of forests: they discover what makes a tree resist drought
An international team, with the participation of INTA and Conicet, discovered that genetics can be decisive for trees to better resist droughts
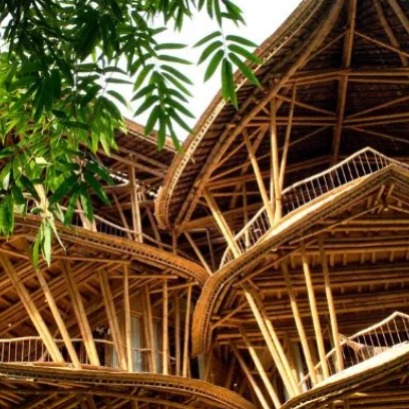 The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
This material that grows in South America creates the most resistant constructions and radically changes the world of architecture One particular building material has been used for millennia by various cultures in South America. This is due to its structural resistance that allows the creation of homes, bridges and shelters. Its archaeological presence shows that it was one of the most valued construction resources in seismic and humid areas.
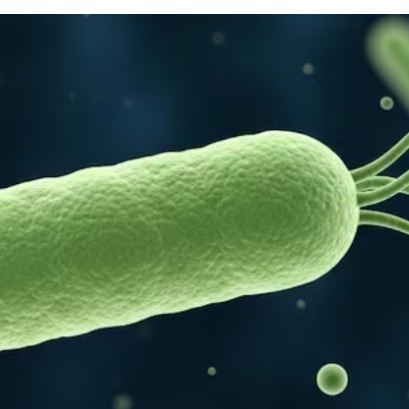 The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
Pioneering study shows trees surprising internal microbial diversity and potential influence on global climate, driving novel strategies for agricultural and forestry management





















