
The mystery of the 400 crooked trees of the Gryfino forest
Poland's enigmatic "crooked forest" combines elements of science fiction with ecological peculiarity, as it is home to hundreds of mysteriously growing pine trees, all with identical curvatures.
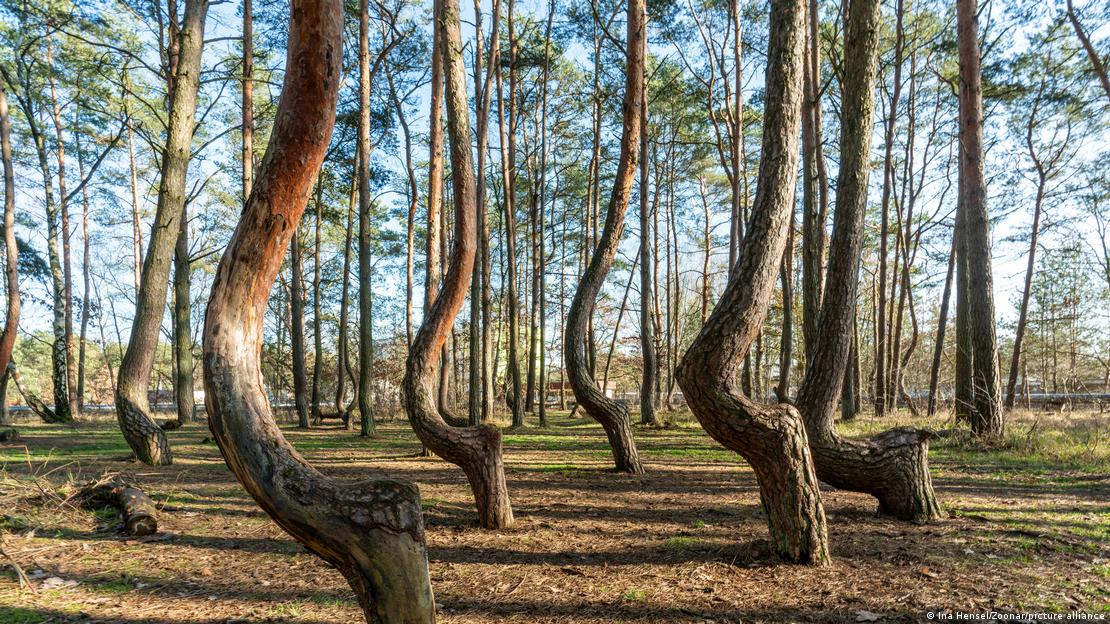
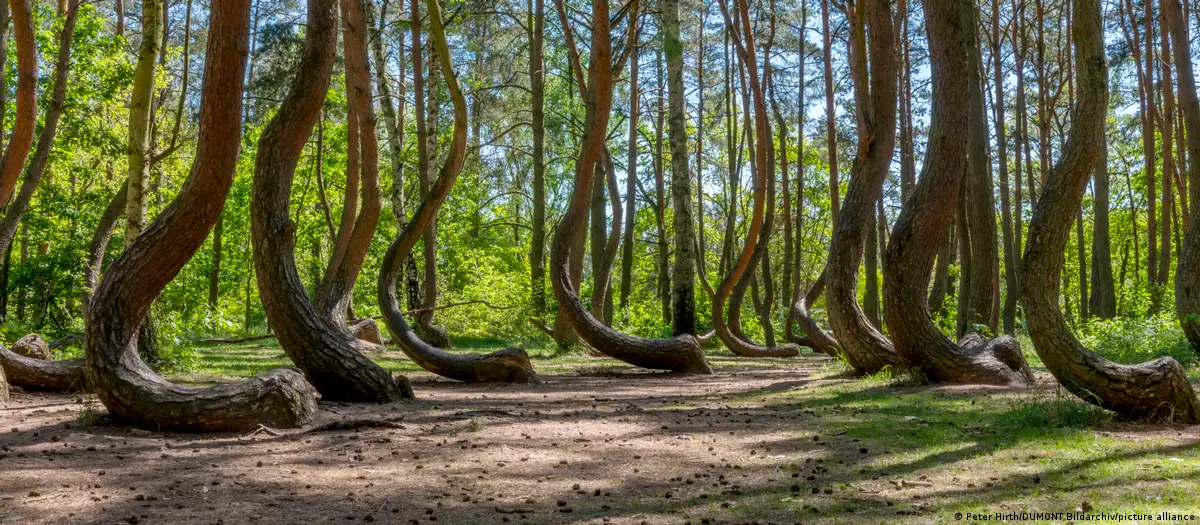
In northwest Poland, in the enigmatic Krzywy Las, lies a natural phenomenon that has baffled scientists and curious people for generations. In this forest, 400 trees seemingly defy the laws of nature, growing with trunks curved at a 90-degree angle, forming an enigmatic figure that resembles the letter J. The most intriguing thing is that most of the trees point towards the North, as if they were following some ancient cosmic calling.
Although there are curved trees in other parts of the world, the quantity and orderly arrangement in this forest is unique, deepening the mystery surrounding the pine trees near the Polish town of Gryfino.
To date, there is no definitive answer to explain the strange shape of these trees, and theories range from the practical to the strange. It is estimated that they were planted in the 1930s, before Gryfino was invaded and destroyed during World War II, leading to the abandonment of the town and the loss of clues as to what may have deformed these trees, as reported by The New York Times in 2017.
Different theories about the Gryfino Crooked Forest
The theories surrounding this enigma are varied and fascinating. Some propose that the trees were buried under a heavy snowstorm during their youth, while others suggest, more incredibly, that they were crushed by Nazi tanks during the war when they were young trees. There is also the possibility, raised by some more realists, that the area's unique gravitational pull has transformed its trunks in unusual ways.
"It seems like a classic response to gravity to me," Gary Coleman, associate professor of Plant Sciences and Landscape Architecture at the University of Maryland, told the Washington Post in 2022. "As long as the stem is horizontal to gravity, the plant has a mechanism by which it can reorient itself," he added.
According to Coleman's assessment, at some point during his youth, these trees leaned horizontally.
"As you can see, the horizontal moment only occurs for a certain amount of time. It seems that it probably occurred when they were quite young seedlings or perhaps small trees, a few meters high," he explained.
Human manipulation
However, the most intriguing explanation, and perhaps the most widely accepted, is that local farmers manipulated the trees after planting them in the 1930s. These farmers are said to have hoped to use the trees to make furniture or boats with curved shapes. , so they intervened when the trees were barely 10 years old. However, World War II in 1939 may have stopped them, ultimately leaving a lasting mark on the landscape.
As to why the trees point north, the truth remains in the shadows. Dr. William Remphrey, a retired plant scientist at the University of Manitoba, interviewed by The New York Times, speculates that this orientation is simply a coincidence without deep meaning.
Although human manipulation seems a plausible explanation, the true nature of the enigma remains uncertain. In the meantime, we are left to marvel at this unusual landscape and wait patiently until someone can one day conclusively unravel the mystery of the Krzywy Las trees.


IT MAY INTEREST YOU
 INTA Delta begins propagation of seven Creole willow clones for ecological restoration in Paraná
INTA Delta begins propagation of seven Creole willow clones for ecological restoration in Paraná
As a result of the rescue, domestication and registration work carried out by Teresa Cerrillo, a leading researcher in Salix Genetic Improvement, within the framework of the National Genetic and Forest Resources Programs of INTA, the multiplication and propagation of seven clones of Creole willow (Salix humboldtiana) began recently registered in the National Seed Institute (INASE) by INTA Delta del Paraná.
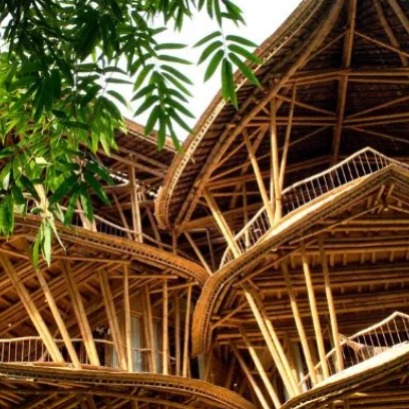 The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
This material that grows in South America creates the most resistant constructions and radically changes the world of architecture One particular building material has been used for millennia by various cultures in South America. This is due to its structural resistance that allows the creation of homes, bridges and shelters. Its archaeological presence shows that it was one of the most valued construction resources in seismic and humid areas.
 The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
Pioneering study shows trees surprising internal microbial diversity and potential influence on global climate, driving novel strategies for agricultural and forestry management





















